Today, the term “cold chain” refers to a temperature-controlled supply chain. A cold chain is a system of refrigerated transportation and storage for temperature-sensitive products, typically food or pharmaceuticals.
A cold chain can be as short as the link between a fishing boat and a processing plant, or it can span the globe, involving multiple shippers, storage facilities, and retailers. In the pharma industry, an uninterrupted cold chain is critical to ensuring that products maintain their efficacy throughout the shipping and storing process.
What is Cold Chain Management (CCM)?
Cold chain management (CCM) is the process of maintaining a product’s cold chain. The cold chain is the system that keeps perishable goods at a temperature that prolongs their shelf life and prevents spoilage. CCM involves the end-to-end process of storing, transporting, and handling products in a way that maintains their quality and safety.
Importance of Cold Chain Management
1. Maintaining product quality and safety:
The primary purpose of CCM is to maintain the quality and safety of perishable goods. By keeping products at the proper temperature, CCM prevents spoilage and foodborne illness.
2. Prolonging shelf life:
CCM also helps to prolong the shelf life of products. By preventing spoilage, CCM allows products to be stored and sold for a longer period of time. With 24/7 monitoring and temperature-controlled transportation, CCM ensures that products remain fresh and safe throughout the supply chain.
3. Reducing waste:
One of the benefits of CCM is that it helps to reduce waste. By preventing spoilage, CCM reduces the amount of food that is thrown away.
4. Improving customer satisfaction:
Your B2B customers and end consumers are looking for high-quality, safe, and fresh products. By ensuring that your products meet these quality standards, CCM can help to improve customer satisfaction.
5. Enhancing brand reputation:
CCM enhances brand reputation by ensuring that products are of the highest quality and safety. By providing safe and high-quality products, CCM helps to build customer trust and loyalty.
6. Increasing profits:
CCM helps to increase profits by reducing waste, extending the shelf life of products, and improving customer satisfaction.
What is the Cold Chain Management Process?
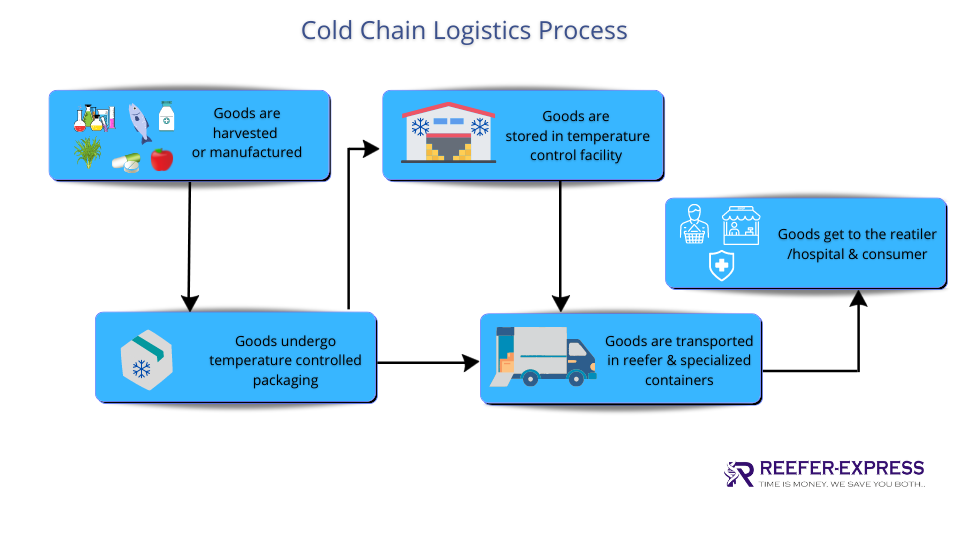
The cold chain management process involves the end-to-end storage and transportation of perishable goods. The process includes four main steps:
1. Planning:
In the planning stage, businesses develop a plan for how they will store and transport their products. They consider factors such as product type, storage requirements, and transportation methods.
2. Implementation:
In the implementation stage, businesses put their plan into action. They establish procedures for storing and transporting products and train employees on how to properly follow these procedures.
3. Monitoring:
In the monitoring stage, businesses track and record data related to the storage and transportation of their products. This data is used to evaluate the performance of the cold chain and identify areas for improvement.
4. Continuous improvement:
In the continuous improvement stage, businesses use data from the monitoring stage to make changes to their cold chain. They implement new procedures and technologies to improve the quality and safety of their products.
The cold chain management process is an ongoing cycle that helps businesses to ensure the quality and safety of their products. By following these four steps, businesses can create a system that meets the needs of their customers.
Cold Chain vs. Supply Chain
The cold chain is a type of supply chain. A supply chain is a system that businesses use to move goods from the supplier to the customer. The cold chain is a subset of the supply chain that focuses on the storage and transportation of perishable goods.
4 differences Between the Cold chain and the Supply chain:
1. Logistics:
The cold chain is a logistics system that businesses use to move perishable goods from the supplier to the customer. The supply chain is a broader term that can refer to any system that businesses use to move goods from the supplier to the customer.
2. Temperature-controlled:
The cold chain is a temperature-controlled logistics system. The supply chain does not necessarily need to be temperature-controlled.
3. Perishable goods:
The cold chain is used to move perishable goods, such as food and pharmaceuticals. The supply chain can be used to move any type of good, including non-perishable items.
4. End-to-end:
The cold chain is an end-to-end system that includes all steps from the supplier to the customer. The supply chain can include any combination of steps, depending on the needs of the business.
Which Products Require Cold Chain Management?
Many different types of products require cold chain management. Some of the most common examples include:
1. Food:
Food is a perishable good that requires cold chain management to extend its shelf life. Without proper storage and transportation, food can spoil quickly and become unsafe to eat.
2. Pharmaceuticals:
Pharmaceuticals are sensitive to temperature and require cold chain management to maintain their efficacy. If pharmaceuticals are not stored and transported properly, they may lose their potency and become ineffective.
3. Chemicals:
Chemicals are often unstable and can be dangerous if not handled properly. Cold chain management helps to ensure that chemicals are transported and stored safely.
4. Blood:
Blood is a perishable product that must be kept at a specific temperature to maintain its quality. Cold chain management is essential for ensuring that blood is safe for transfusions.
5. Organs:
Organs are sensitive to temperature and must be transported quickly to prevent cell death. Cold chain management is essential for organ transplantation.
FAQ’s Cold Chain Management
Q. What is the equipment of the cold chain?
A. The equipment of the cold chain typically includes refrigerated trucks, storage facilities, and temperature-controlled packaging.
Q. What are the key components of the cold chain?
A. The key components of the cold chain are temperature-controlled storage and transportation, trained personnel, and quality assurance procedures.
Q. How can the risk of cold chain management be reduced?
A. The risk of cold chain management can be reduced by ensuring that all equipment is properly maintained and monitored, and by following good practices for storage and transportation.






